Basics: Loadbalancing with NGINX
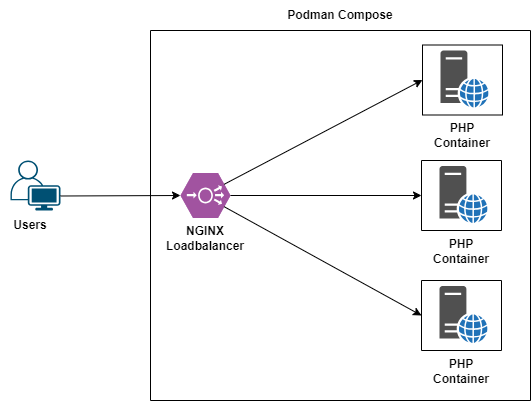
In this guide, we will walk through the steps to set up a simple load balancing environment using NGINX and Podman. This setup will distribute traffic across multiple instances of a PHP web application in round robin mode.
Prerequisites
- Podman installed
- Podman compose installed
An instruction for Ubuntu 22.04 can be found here.
Setup
The complete example can be found on GitHub.
First, let’s structure our project directory as follows:
.
├── app
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── index.php
├── compose.yaml
└── nginx
└── nginx.conf
The App: Simple php Web Interface
Create a simple PHP web interface that shows the current hostname in app/index.php:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hostname Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to the Server</h1>
<p>Served from: <strong><?php echo gethostname(); ?></strong></p>
</body>
</html>
The App: Dockerfile
Create a Dockerfile in app/Dockerfile to build the PHP application:
FROM php:8.2-apache
COPY index.php /var/www/html/
NGINX Configuration
Create an NGINX configuration file in nginx/nginx.conf:
events {}
http {
upstream backend {
server app1:80;
server app2:80;
server app3:80;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
# Backend-Hostname als Header übergeben
proxy_set_header X-Backend-Hostname $upstream_addr;
}
}
}
Compose everything
Create a compose.yaml file to define the services:
version: "3.9"
networks:
default:
name: loadbalancer1_default
services:
app1:
build:
context: ./app
container_name: app1
hostname: app1
ports:
- "8081:80"
app2:
build:
context: ./app
container_name: app2
hostname: app2
ports:
- "8082:80"
app3:
build:
context: ./app
container_name: app3
hostname: app3
ports:
- "8083:80"
loadbalancer:
image: docker.io/nginx:alpine
container_name: loadbalancer
ports:
- "8080:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
depends_on:
- app1
- app2
- app3
Start and test
To start the environment, run:
podman-compose up
Then, open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080/. You should see the PHP web interface served from different backend servers, demonstrating the load balancing setup.
Conclusion and Key Learnings
In this guide, we have set up a basic load balancing environment using NGINX and Podman. Here are the key learnings from this exercise:
- Containerization with Podman: We learned how to containerize a simple PHP application using Podman.
- Load Balancing with NGINX: We configured NGINX to distribute traffic across multiple instances of our PHP application.
- Service Composition with Podman Compose: We used Podman Compose to define and manage multiple services, making it easier to orchestrate our application and load balancer.
- Practical Networking: We explored how to set up networking between containers to enable communication and load balancing.
With these steps, you have a foundational understanding of how to set up load balancing for containerized applications using NGINX and Podman. This setup can be expanded and customized further based on your requirements.